Step 1: fitting the null logistic/linear mixed model
- For binary traits, a null logistic mixed model will be fitted (–traitType=binary).
- For quantitative traits, a null linear mixed model will be fitted (–traitType=quantitative) and needs to be inverse normalized (–invNormalize=TRUE)
-
By default, covariates are included as offset in the model, use –isCovariateOffset=FALSE to deactivate this feature. It will cost more computation time with –isCovariateOffset=FALSE
- The example scripts are located in the extdata folder [https://github.com/saigegit/SAIGE/tree/main/extdata]
#go to the folder
cd extdata
#check the help info for step 1
Rscript step1_fitNULLGLMM.R --help
Fit the null model using a full GRM
For binary traits, a null logistic mixed model will be fitted (–traitType=binary).
- Use –qCovarColList to list categorical covariates. Dummy variables will be created for different levels.
- Use –nThreads for number of CPUs to use
Rscript step1_fitNULLGLMM.R \
--plinkFile=./input/nfam_100_nindep_0_step1_includeMoreRareVariants_poly_22chr \
--phenoFile=./input/pheno_1000samples.txt_withdosages_withBothTraitTypes.txt \
--phenoCol=y_binary \
--covarColList=x1,x2 \
--qCovarColList=x2 \
--sampleIDColinphenoFile=IID \
--traitType=binary \
--outputPrefix=./output/example_binary \
--nThreads=24 \
--IsOverwriteVarianceRatioFile=TRUE
For quantitative traits, a null linear mixed model will be fitted (–traitType=quantitative) and needs to be inverse normalized (–invNormalize=TRUE)
Rscript step1_fitNULLGLMM.R \
--plinkFile=./input/nfam_100_nindep_0_step1_includeMoreRareVariants_poly_22chr \
--useSparseGRMtoFitNULL=FALSE \
--phenoFile=./input/pheno_1000samples.txt_withdosages_withBothTraitTypes.txt \
--phenoCol=y_quantitative \
--covarColList=x1,x2 \
--qCovarColList=x2 \
--sampleIDColinphenoFile=IID \
--invNormalize=TRUE \
--traitType=quantitative \
--outputPrefix=./output/example_quantitative \
--nThreads=24 \
--IsOverwriteVarianceRatioFile=TRUE
Fit the null model using a sparse GRM (only one CPU will be used)
- Use –useSparseGRMtoFitNULL=TRUE
- Use –sparseGRMFile for the file containing the sparse GRM
- Use –sparseGRMSampleIDFile for the file containing the IDs for samples in the sparse GRM
- To only include a subset of samples to fit the null model, use –SampleIDIncludeFile
- Only one CPU will be used and LOCO won’t be applied
Estimating variance ratio with random markers. This will speed up Step 2 with a fast test (set is_fastTest=TRUE in Step 2)
- Use –skipVarianceRatioEstimation=FALSE
- Specify the plink file containing markers that will be used for variance ratio estimation with –plinkFile. e.g. –plinkFile=./input/nfam_100_nindep_0_step1_includeMoreRareVariants_poly_22chr
- Only a small subset of randomly selected markers are needed in the plink file. e.g. –plinkFile=./input/nfam_100_nindep_0_step1_includeMoreRareVariants_poly_22chr_random1000. This can reduce the memory usage for reading in plink file.
#(Optional) get ids for 1000 random markers
shuf -n 1000 ./input/nfam_100_nindep_0_step1_includeMoreRareVariants_poly_22chr.bim | awk '{print $2}' > ./input/nfam_100_nindep_0_step1_includeMoreRareVariants_poly_22chr.1000Markers.list
#(Optional)make a new plink file containing those 1000 markers
plink2 --bfile ./input/nfam_100_nindep_0_step1_includeMoreRareVariants_poly_22chr --extract ./input/nfam_100_nindep_0_step1_includeMoreRareVariants_poly_22chr.1000Markers.list --make-bed --out ./input/nfam_100_nindep_0_step1_includeMoreRareVariants_poly_22chr_random1000
#Fit the null model and estimate a variance ratio
Rscript step1_fitNULLGLMM.R \
--sparseGRMFile=output/sparseGRM_relatednessCutoff_0.125_1000_randomMarkersUsed.sparseGRM.mtx \
--sparseGRMSampleIDFile=output/sparseGRM_relatednessCutoff_0.125_1000_randomMarkersUsed.sparseGRM.mtx.sampleIDs.txt \
--useSparseGRMtoFitNULL=TRUE \
--plinkFile=./input/nfam_100_nindep_0_step1_includeMoreRareVariants_poly_22chr_random1000 \
--phenoFile=./input/pheno_1000samples.txt_withdosages_withBothTraitTypes.txt \
--skipVarianceRatioEstimation=FALSE \
--phenoCol=y_binary \
--covarColList=x1,x2 \
--qCovarColList=x2 \
--sampleIDColinphenoFile=IID \
--traitType=binary \
--outputPrefix=./output/example_binary_sparseGRM_vr \
--IsOverwriteVarianceRatioFile=TRUE
Do not estiamte the variance ratio. –plinkFile is not specified
WARNING: We do not recomment this option, because the computaiton cost is not optimal for Step 2.
Rscript step1_fitNULLGLMM.R \
--sparseGRMFile=output/sparseGRM_relatednessCutoff_0.125_1000_randomMarkersUsed.sparseGRM.mtx \
--sparseGRMSampleIDFile=output/sparseGRM_relatednessCutoff_0.125_1000_randomMarkersUsed.sparseGRM.mtx.sampleIDs.txt \
--useSparseGRMtoFitNULL=TRUE \
--phenoFile=./input/pheno_1000samples.txt_withdosages_withBothTraitTypes.txt \
--phenoCol=y_binary \
--covarColList=x1,x2 \
--qCovarColList=x2 \
--sampleIDColinphenoFile=IID \
--traitType=binary \
--outputPrefix=./output/example_binary_sparseGRMforNull_no_vr \
--IsOverwriteVarianceRatioFile=TRUE
Input files
- (Required) Phenotype file (contains covariates if any, such as gender and age) The file can be either space or tab-delimited with a header. It is required that the file contains one column for sample IDs and one column for the phenotype. It may contain columns for covariates.
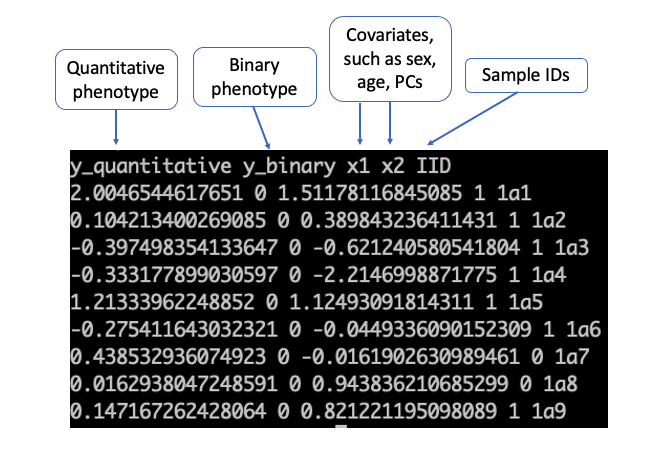
```
less -S ./input/pheno_1000samples.txt_withdosages_withBothTraitTypes.txt
```
-
(Optional) Genotype file for constructing the full genetic relationship matrix (GRM) and estimating the variance ratio
SAIGE takes the PLINK binary file for the genotypes and assumes the file prefix is the same one for .bed, .bim. and .fam./input/nfam_100_nindep_0_step1_includeMoreRareVariants_poly.bed ./input/nfam_100_nindep_0_step1_includeMoreRareVariants_poly.bim ./input/nfam_100_nindep_0_step1_includeMoreRareVariants_poly.fam -
(Optional) sparse GRM file and the sample ID file for the sparse GRM. Please see Step 0 for more details.
./output/sparseGRM_relatednessCutoff_0.125_1000_randomMarkersUsed.sparseGRM.mtx ./output/sparseGRM_relatednessCutoff_0.125_1000_randomMarkersUsed.sparseGRM.mtx.sampleIDs.txt ##the sparse matrix can be read and viewed using the R library Matrix library(Matrix) sparseGRM = readMM("./output/sparseGRM_relatednessCutoff_0.125_1000_randomMarkersUsed.sparseGRM.mtx")
Output files
-
model file (input for Step 2)
./output/example_quantitative.rda #load the model file in R load("./output/example_quantitative.rda") names(modglmm) modglmm$theta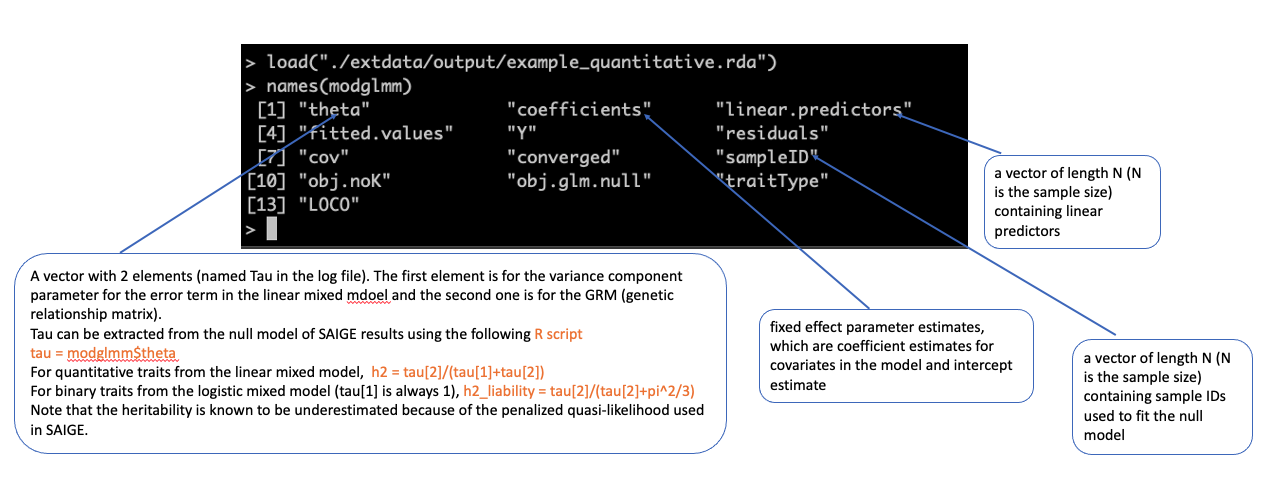
-
variance ratio file (if variance ratio is estiamted in Step 1, this will be input for Step 2)
less -S ./output/example_quantitative.varianceRatio.txt